Basics
- Access Modifiers
- Basic Concepts
- Build Task
- Compiling Manually
- Creating Paths
- Hierarchy
- http-server
- package.json
- Simple Example
- tsconfig.json - the /TypeScript project file
- tsconfig.json - multiple files
- Strict Null Checks
- Type Annotations
- Type Assertions
- TypeScript features
Challenges
Classes
- Abstract Classes
- Basics and Features
- Car Class Demo
- Class Fields
- Class Properties
- Constructors
- Inheritance (extends) Demo
- Function as Class Property
- instantiating new objects
- Spaceship Class Blueprint Demo
Debugging
Events
External Files
Flow Control
Forms
Functions
- Arrow Functions
- Arrow Functions 'this'
- Function Examples
- Function Scope Example
- Function with default arg values
- Function Types
- Global Functions
- Lambdas
- Optional Arguments
- Simple Arrow Functions Example
Html Elements
Installation
Interfaces
- Basics
- Duck Typing
- Employee Interface Example
- Implements vs Extends
- Interface Spaceship Contract Example
- Configuration Contract Example
Keywords
Modules
Namespaces
Operators
Reference Files
String
Types
TypeScript - static
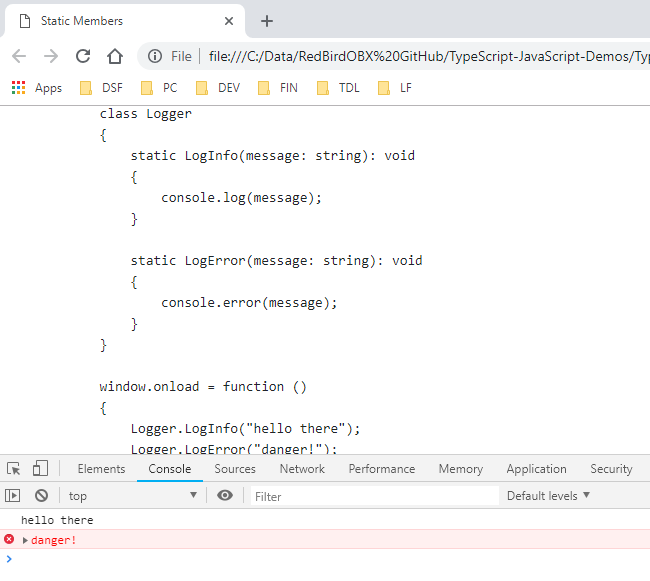
In TypeScript, you cannot define an entire class as static but you can however define it's members.
When you do this, you do not need to instantiate a new object to access those members.
When members of a class are public (not static), you access them using the this keyword.
When members of a class are static, you call them by prefixing the call with the class name and non the
this keyword...even within the same class.
class Logger
{
static LogInfo(message: string): void
{
console.log(message);
}
static LogError(message: string): void
{
console.error(message);
// see how we call it by using the class name instead of 'this'?
Logger.LogInfo("An error occurred...");
}
}
window.onload = function ()
{
// see how I didn't need to instantiate the class as an object?
Logger.LogInfo("hello there");
Logger.LogError("danger!");
};